Introduction
Business need is a proposal idea for Motorway software. It is a sole or multiple brand specific evaluated, prioritized and approved document which describes in the level of detail why, how and how much desired development should help to improve brand’s growth measured in some well-known metrics (KPI).
Business need in its nature can be long-lasting or temporary, money-saving or solution which can bring up opportunities. It could also cause conflicts in some other business areas if not analyzed and prioritized properly or put on hold the company’s wider strategy plan.
Therefore, it is crucial to make sure that the business need input is sufficient, and each step is critically analyzed. The purpose of this document is to help to avoid any kind of derivations which cannot be part of Motorway software.
Addition to other relevant information business need proposal should contain following:
1. Evaluation
1.2 Minimum viable product
The first evaluation step should be comparing the desired problem-solving solution with the existing solution available. The minimum viable product (MVP) is a basic (existing) model which can help to solve the problem at its very base level. It helps to understand the solution steps of the problem, because this will play an important role in wider analyzing.
For example: to share not so sensitive information with our colleagues can be done by using Google Sheets? Or do we need special development to contact 500 customers? Maybe our calling center can do the job?
1.3 Time factor
Analysis must consist of a problem’s lasting nature. It is important to understand do we deal with permanent or temporary kinds of issues.
For example:
a) there are many already registered cars in stock which are required to show on a website as new cars. As importer would suffer with this issue enormously it still cannot be listed as permanent because in long-term it is not sustainable way for automotive industry to handle its business,
b) dealers should be able to see cars cross-country – if it’s the importer’s business decision then yes, it can be considered as a permanent solution.
1.4 Time criticality
Under this point it required to be evaluated how time critical is delivery of proposed solution. Two extremums are show-stopper and nice-to-have. All others should be positioned in between these two.
For example:
a) VAT % to be changed on 1st of January – as it is mandatory by the law, it is absolutely a time critical issue. It is also one of the exemptions as it has exact deadline,
b) factory integration regarding service campaigns doesn’t work – time critical as it can potentially cause huge losses,
c) dealers can’t book cars cross-country – it should be considered low or nice-to-have functionality as there are multiple workarounds.
1.5 Conflicts
Group companies can have different departments between which the desired solution could potentially be conflicted. Moreover, the same level departments (two or more importers) should have their word of saying in every proposal for higher reach. A solution which will be fitted to one importer will not always be perfect to another and therefore needs global analysis.
For example:
One importer would like to show in the configurator similar in-stock cars available. Others decline because their core business is only to sell factory orders. It cannot be solved without compromise (or derivation).
1.6 Evidence
Evidence that the business need will be beneficial with KPI metering involved. Further analysis will take account and compare development versus human resources.
For example:
Solution would help with the automation of the use of human resources daily. Estimation of 110 users make operation 5 days a week daily with 10 minutes per person operation timing with total. KPI human resources vs automation. Calculation: 110 persons x 10 minutes per operations x 5 days = 91,66667 hours of human resources will be saved per week.
2. Prioritization
All business needs cannot be equally important and therefore global prioritization is needed.
2.1 Prioritization made by department
We suggest each department list their business needs proposals in their relevancy order based on the matrix described in Evaluation paragraph. After internal analysis, the overall business need proposal should be created.
For example:
a) in minimum viable product (MVP) exists issue, which is not permanent in its nature, but it is time critical and have no conflicts with other departments – this issue can be solved without business need by department itself,
b) there are no MVP available for an issue permanent issue, this would cause huge losses but might have some conflicts with other departments – problem solving should be started consultation with other departments to understand do they have the same issue.
2.2 Prioritization made by management
Following the wider company strategy, department-based prioritized proposals must be structurally put in order by management. The issue which impedes one department might not be affected by other departments, or it is not important enough to commit an effort.
For example:
One brand importer has a serious issue with its factory integration but at the same time a bigger (and more profitable) department has an issue which is not that serious in its nature but business-wise is more important.
2.3 Prioritization models
There are multiple models and best practices available on how to prioritize different business needs at any level. Following are only one of the examples how multiple business needs can be measured internally in the different aspects:
For example:
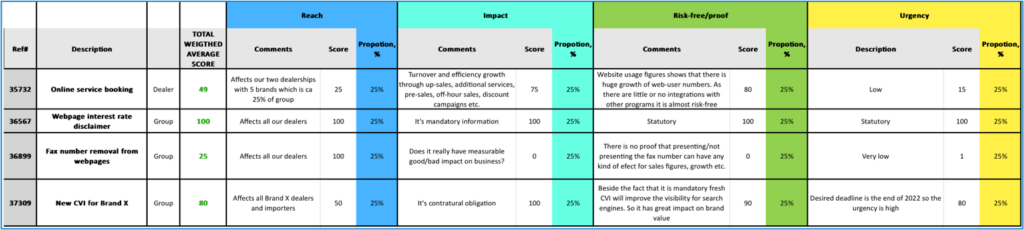
Business needs are listed, and the total weighted average score is calculated by using 4 aspects which are all set to be equal in this case:
- Reach – evaluates how many people, departments, dealerships, etc., are involved.
- Input – evaluates why this business is important. Is it set by the law (statutory) or is it something which can improve sales figures?
- Risk free/proof – is there any proof that it will improve our business? It can be also looked at as a risk-free index.
- Urgency – how critical this business need is.
As it appears the removal of the fax number from websites can affect all the people in the group, but it is totally irrelevant in other respects. Otherwise, the new CVI performs strongly because at first-hand it is mandatory for contractual reasons, it is also better reachable for search engines. Showing leasing information disclaimer is statutory and mandatory by law, so its importance is 100%.
3. Approval
3.1 Customer approval
After previous steps Evaluation and Prioritization concluded, the list of business proposals is ready for presenting to Motorway team.
3.2 Developer approval
The developer would analyze the proposed business need and make its initial proposal on how the issues could be solved. Developers also decide whether the business need proposal is consistent with Motorway.
Compiled by Motorway Software
